Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Size and Forecast – 2026 – 2033
The Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices Market is projected to grow from about USD 1.2 billion in 2026 to USD 2.3 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of ~7.5 % between 2026 and 2033 due to rising GERD prevalence and demand for minimally invasive treatments.
Global Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Overview
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) treatment devices are medical technologies designed to reduce acid reflux and manage chronic GERD symptoms when lifestyle changes or medications are insufficient. These devices primarily work by strengthening or supporting the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Common options include magnetic sphincter augmentation systems, endoscopic suturing or radiofrequency devices, and implantable mechanical barriers. GERD treatment devices offer minimally invasive alternatives to traditional surgery, aiming to improve symptom control, reduce dependence on long-term medications, and enhance quality of life for patients with persistent or severe reflux disease.
Key Takeaways
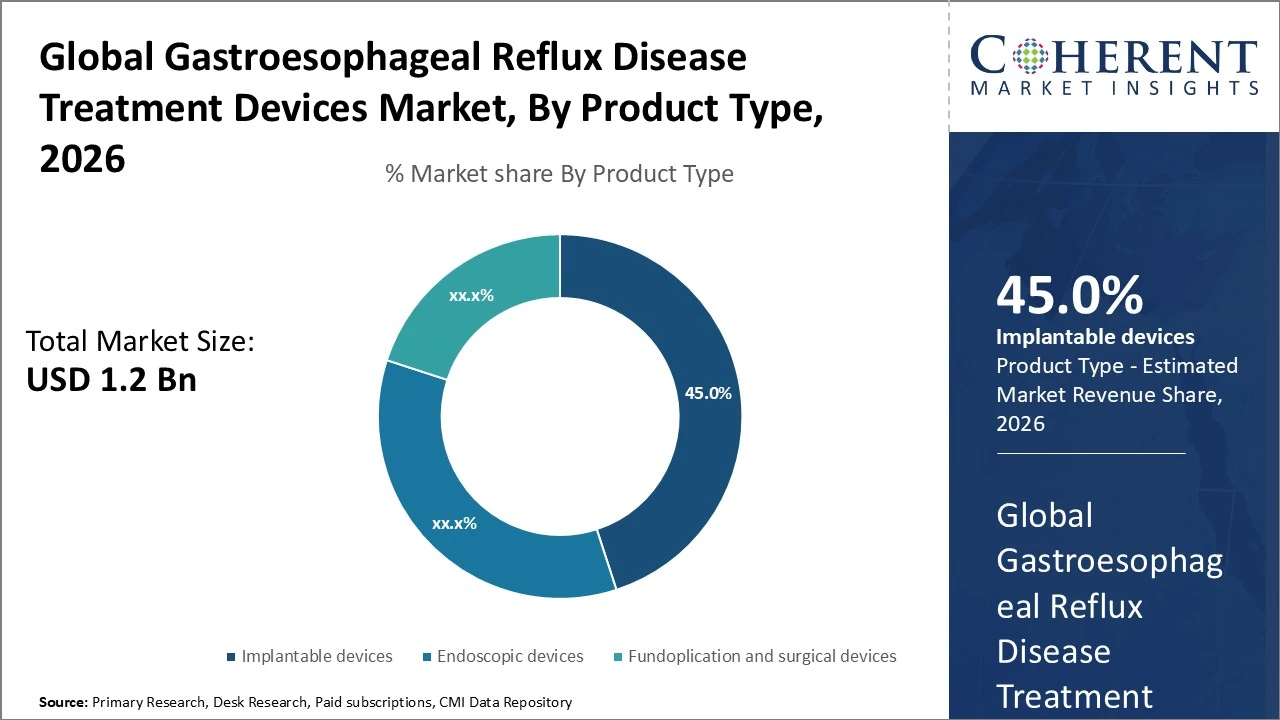
Product Type, implantable devices hold the largest share of 45%.
Hospitals dominate end‑user share with around 60%.
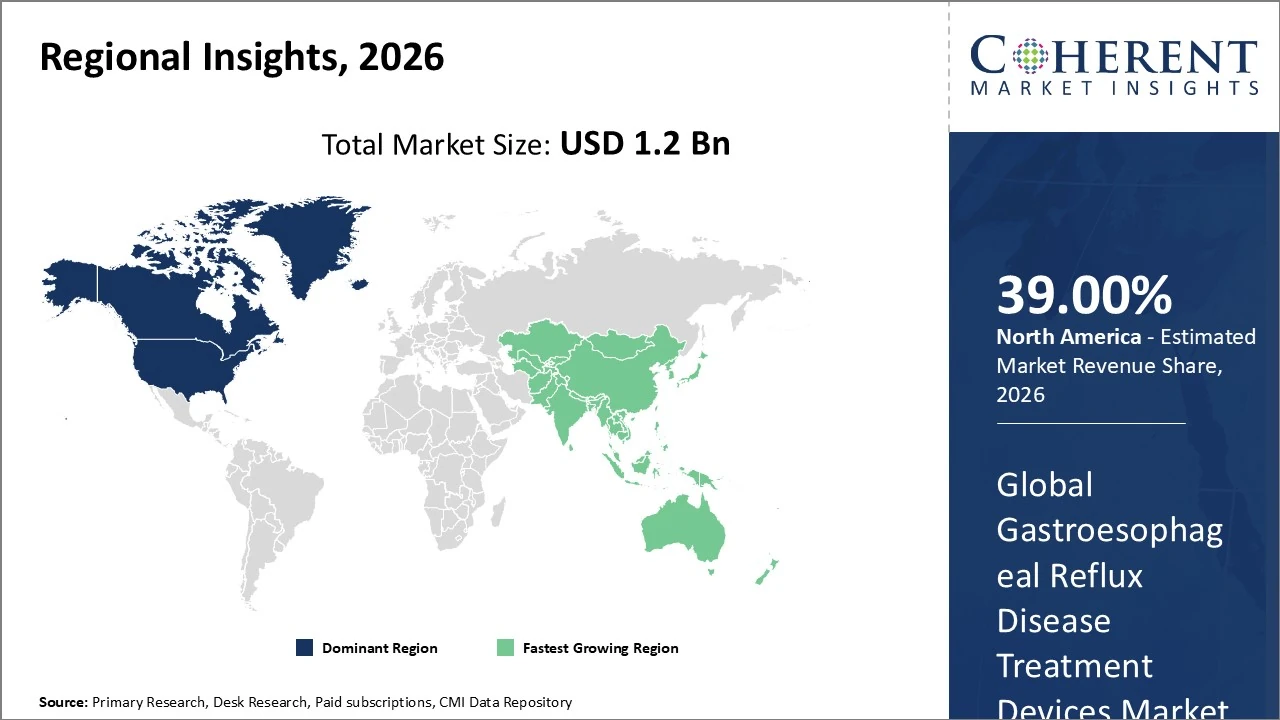
North America dominates the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market, holding about 39% of global share.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Segmentation Analysis
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Insights, By Product Type
The Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is segmented by product type into implantable devices, endoscopic devices, fundoplication devices and others. Implantable devices hold the largest share, 45%, due to their durable effectiveness and growing adoption. Endoscopic devices follow with around 35% share, driven by demand for minimally invasive procedures. Fundoplication and surgical devices constitute 20% but remain significant for refractory cases. Emerging technologies like radiofrequency ablation and electrical stimulation are part of the others segment, contributing the remaining share and expected to grow fastest.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Insights, By End-User
In the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market, hospitals dominate end‑user share with around 60% due to comprehensive care, advanced infrastructure, and capacity for complex procedures. Clinics/specialty gastroenterology centers hold roughly 30%, supported by focused outpatient management and rising awareness. Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) account for about 10%, growing fastest as minimally invasive, same‑day procedures become more popular for cost‑effective GERD interventions.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Trends
Increasing adoption of endoscopic therapies and magnetic sphincter augmentation devices is reducing recovery time and hospital stays.
Emergence of advanced devices such as radiofrequency ablation systems and electrical stimulators is improving treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
Growth of outpatient clinics and ambulatory surgical centers is making GERD device therapies more accessible, cost-effective, and convenient for patients.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Insights, By Geography
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample
North America Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Analysis and Trends
North America dominates the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market, holding about 39% of global share due to high GERD prevalence, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and early adoption of minimally invasive technologies. The United States is the key contributor within the region, supported by favorable reimbursement policies and strong clinical adoption of innovative devices like magnetic sphincter augmentation and endoscopic systems. Demand is driven by increased awareness, robust R&D, and patient preference for less invasive procedures. Continued investment in device innovation and strong diagnostic capabilities are expected to sustain North America’s leadership through the forecast period.
Asia Pacific Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Analysis and Trends
The Asia Pacific GERD Treatment Devices market holds around 20% of global market share, emerging as the fastest‑growing region due to rising GERD prevalence, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increased disposable income in key countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Growth is propelled by greater disease awareness, expanding access to minimally invasive procedures, and investments in gastroenterology facilities. Urban lifestyle changes and higher obesity rates are boosting demand for advanced treatment devices. The region is expected to maintain strong growth through 2033 as healthcare access deepens and adoption of innovative endoscopic and implantable therapies expands.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Outlook for Key Countries
USA Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Analysis and Trends
The United States leads the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market, contributing approximately ~25% of the global market share within North America, the region holding roughly 39% overall due to high disease prevalence and advanced care infrastructure. Growth is driven by widespread adoption of minimally invasive technologies such as magnetic sphincter augmentation and endoscopic devices, favorable reimbursement policies, and strong clinical awareness among gastroenterologists. The U.S. market is expanding at a solid CAGR (5%+ forecast) supported by innovation, rising obesity‑linked GERD cases, and increasing patient preference for non‑pharmacologic interventions.
Germany Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Analysis and Trends
The Germany Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is a key part of Europe’s expanding device landscape, characterized by steady growth driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and medical technology investment. Germany’s market is projected to grow at a moderate CAGR (~5.3%) through the coming decade, reflecting increased adoption of minimally invasive and diagnostic devices and strong clinical capabilities. ?? Hospitals and specialized centres lead device utilization, supported by public and private collaborations in R&D. Germany’s emphasis on innovation and early diagnosis enhances treatment efficacy, though cost and reimbursement constraints may temper rapid uptake compared to North America.
Analyst Opinion
Rising GERD prevalence globally and increasing patient awareness are expected to drive consistent market expansion.
Analysts emphasize that endoscopic therapies and magnetic sphincter augmentation devices are replacing traditional surgical approaches due to faster recovery and fewer complications.
Emerging technologies like radiofrequency ablation and electrical stimulation are expected to capture niche segments and boost market value.
North America dominates, while Asia-Pacific offers the fastest growth due to improving healthcare infrastructure and rising obesity rates.
High device costs, stringent regulatory approvals, and reimbursement limitations may slow adoption in price-sensitive regions.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2025 | Market Size in 2026: | USD 1.2 Billion |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2026 To 2033 |
| Forecast Period 2026 to 2033 CAGR: | 7.5% | 2033 Value Projection: | USD 2.3 Billion |
| Geographies covered: |
|
||
| Segments covered: |
|
||
| Companies covered: | Medtronic, EndoGastric Solutions, Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Olympus Corporation, Mederi Therapeutics, and Apollo Endosurgery | ||
| Growth Drivers: |
|
||
Uncover macros and micros vetted on 75+ parameters: Get instant access to report
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Growth Factors
The Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is growing due to several key factors. Rising GERD prevalence globally, driven by obesity, poor diet, and lifestyle changes, increases demand for effective treatments. Patient preference for minimally invasive procedures like endoscopic therapies and magnetic sphincter augmentation fuels adoption. Technological advancements in device design improve safety, efficacy, and patient outcomes. Expanding healthcare infrastructure, especially in emerging economies, enhances accessibility. Favorable reimbursement policies and growing awareness among gastroenterologists and patients further accelerate market growth. Additionally, increased R&D investments by leading companies support innovation, sustaining long-term expansion of the device market.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Development
The Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation and patient-centric approaches. Companies are focusing on minimally invasive solutions, including magnetic sphincter augmentation, endoscopic therapies, and radiofrequency ablation devices, to reduce recovery time and improve outcomes. Strategic partnerships, acquisitions, and clinical trials are accelerating product development and market penetration. Emerging regions like Asia-Pacific and Latin America are receiving increased attention due to growing GERD prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Ongoing R&D, coupled with regulatory approvals and reimbursement support, is enabling the development of next-generation devices, making GERD management more efficient and accessible worldwide.
Key Players
Leading Companies of the Market
Medtronic
EndoGastric Solutions
Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson)
Olympus Corporation
Mederi Therapeutics
Apollo Endosurgery
The Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is dominated by companies such as Medtronic, EndoGastric Solutions, Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson), Olympus Corporation, Mederi Therapeutics, and Apollo Endosurgery. These leaders drive innovation through minimally invasive devices, magnetic sphincter augmentation, and endoscopic therapies, maintaining strong global presence and strategic partnerships across hospitals and outpatient centers.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Future Outlook
The future of the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market is poised for robust growth, driven by rising disease prevalence, obesity, and lifestyle-related risk factors globally. Analysts anticipate continued adoption of minimally invasive technologies, including magnetic sphincter augmentation, endoscopic procedures, and radiofrequency ablation, which offer safer and faster recovery options. Expansion into emerging markets like Asia-Pacific and Latin America will further fuel growth, supported by improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing patient awareness. Continuous R&D, technological innovation, and favorable reimbursement policies are expected to enhance treatment efficacy, accessibility, and affordability, positioning the market for sustained long-term expansion through 2033.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment Devices Market Historical Analysis
Historically, the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Treatment Devices market has evolved from traditional surgical interventions, such as laparoscopic fundoplication, to minimally invasive and device-based therapies. Over the past decade, endoscopic procedures and magnetic sphincter augmentation systems gained prominence, driven by patient preference for faster recovery and reduced complications. North America dominated early adoption due to advanced healthcare infrastructure and clinical awareness, while Europe followed closely. Growth in emerging regions was initially slow due to limited access and higher costs. The market’s historical expansion reflects technological innovation, increasing GERD prevalence, and rising focus on outpatient and non-pharmacologic management options.
Sources
Primary Research Interviews:
Medical Device Manufacturers & Executives
Healthcare Professionals
Hospital & Clinic Administrators
Regulatory & Reimbursement Experts
Databases:
PubMed / Medline
ClinicalTrials.gov
WHO Global Health Observatory
Journals:
Gastroenterology
Surgical Endoscopy
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery
Endoscopy
Newspapers:
The Wall Street Journal
Financial Times
Economic Times
The New York Times
Associations:
International Society for Diseases of the Esophagus (ISDE)
World Gastroenterology Organisation (WGO)
American Gastroenterological Association (AGA)
American College of Gastroenterology (ACG)
Share
Share
About Author
Manisha Vibhute is a consultant with over 5 years of experience in market research and consulting. With a strong understanding of market dynamics, Manisha assists clients in developing effective market access strategies. She helps medical device companies navigate pricing, reimbursement, and regulatory pathways to ensure successful product launches.
Missing comfort of reading report in your local language? Find your preferred language :
Transform your Strategy with Exclusive Trending Reports :
Frequently Asked Questions
Select a License Type
Joining thousands of companies around the world committed to making the Excellent Business Solutions.
View All Our Clients