Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Size and Forecast – 2025 – 2032
The Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market size is estimated to be valued at USD 3.85 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 9.75 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.8% from 2025 to 2032.
Global Direct To Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Overview
Genetic testing is a type of medical test that determines changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins. The tests were available only through healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and genetic counselors. However, this trend is gradually shifting towards the customer or consumer. Genetic testing is now offered directly at home, and is called Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Genetic Testing, which bypasses the mediators or facilitators such as Physicians, Genetic Counselors, and others. The most critical thing about the genetic tests is that these tests are for disease susceptibilities only and cannot be used alone for treatment decisions or other medical interventions. In genetic testing, interpretation is important and is transferred to individual patient, who may not be trained geneticist.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Genetic Testing is advantageous for manufacturers as it gives direct access to them to appeal to the customer and maximize their revenue. However, this testing provides easy access to the customer while chances of misinterpretation are really high.
The U.S. FDA has kept these tests in “Tier 3” category due to high chances of misinterpretation of direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic testing. According to FDA, Tier 3 category means that there is no clinical validity or utility of such Distribution Channels in healthy individuals in the population.
Key Takeaways
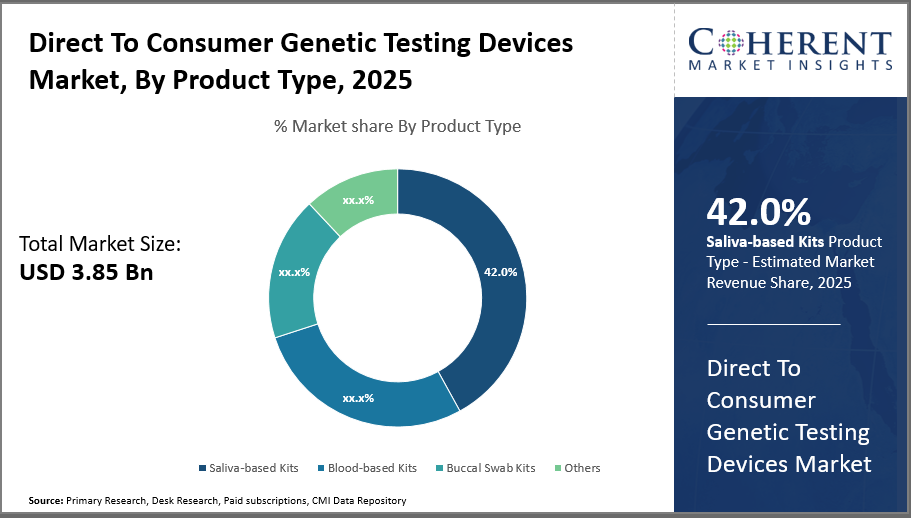
Saliva-based kits dominate the product segment with a 42% industry share owing to their non-invasive collection method and consumer convenience, while blood-based kits show promising growth due to higher accuracy and expanding clinical Distribution Channels.
The online retail distribution channel commands a majority share reflecting consumer preference for direct-to-door affordability and access, supported by increasing digital literacy.
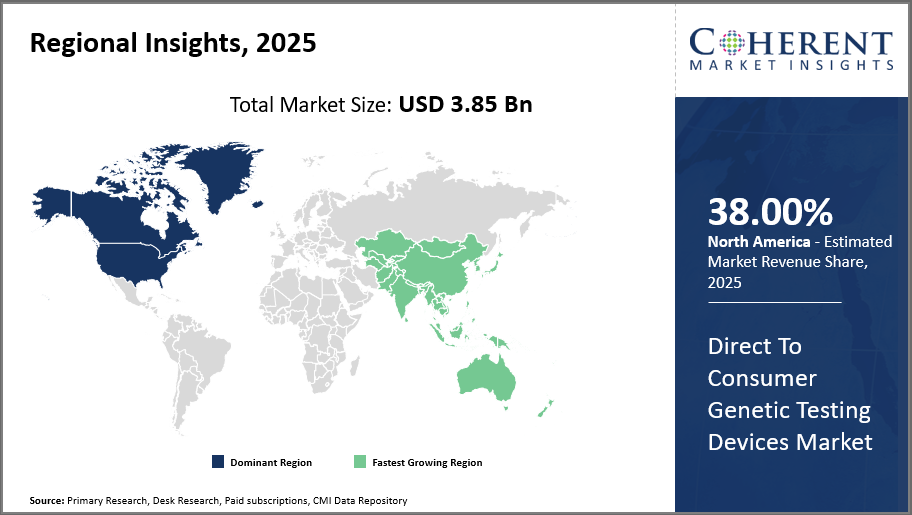
North America leads the regional market driven by high consumer awareness and supportive regulations, capturing over 38% market share.
Asia Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing market with a CAGR surpassing 16%, buoyed by rising disposable incomes, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasingly tech-savvy populations.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market – Segmentation Analysis
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Insights, By Product Type
In terms of product type, saliva-based kits dominate the market share with 42%. Saliva-based Kits lead due to non-invasive, user-friendly collection methods and cost-efficiency, making them highly preferred by consumers for ancestry and lifestyle genetic testing. This segment holds a substantial share of the market due to the high consumer preference for hassle-free, non-invasive collection methods compared to blood or tissue samples. The ease of saliva sample collection through simple spit or swab methods has made it the most popular choice among genetic testing consumers, driving its strong growth.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Insights, By Application
According to the application segment, health & disease risk assessment commands the largest market share due to increasing consumer demand for preventive health intelligence and personalized treatment pathways. This segment’s growth is underpinned by expanded clinical validation and incorporation of polygenic risk scores in 2025. Customers in this market can take proactive control of their health and obtain tailored insights regarding possible genetic risks without the involvement of healthcare providers. The rise in genetically linked diseases, improvements in genetic testing technologies, and growing consumer awareness are driving its expansion.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Insights, By Distribution Channel
Online Retail segment dominates the market share. Consumer preference for direct, convenient access to these devices via digital platforms combined with competitive pricing models has solidified online retailing as the prime channel. Further, Customers can obtain genetic testing kits online from the comfort of their own homes, and they can access the results via safe online portals. Increased digital adoption, particularly sped up by the consumers ease in comparing products, reading reviews, and accessing discounts are other factors driving this channel's rise.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Trends
The Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices market is witnessing a notable shift towards multi-omics integration, where genetic data is combined with proteomics and metabolomics for holistic health profiling.
For instance, 2024 saw the launch of test kits that incorporate epigenetic markers, adding predictive power to traditional genotyping. Another emerging trend is the rise of subscription-based models offering periodic updates as genetic research advances, ensuring consumers receive evolving insights over time. Additionally, privacy-preserving solutions centered around blockchain technology have started gaining traction, addressing growing concerns in data security and compliance with global privacy standards.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Insights, By Geography
To learn more about this report, Download Free Sample
North America Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Analysis and Trends
The market domination of Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices in North America is driven by a favorable regulatory environment, significant consumer health awareness, and the presence of major industry players like 23andMe and AncestryDNA, both of which have their headquarters in the United States. Because of its vast infrastructure, which facilitates smooth distribution and effective after-sales services, the area accounts for more than 38% of the market.
Asia Pacific Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Analysis and Trends
Asia Pacific, on the other hand, is growing at the quickest rate, with a CAGR of more than sixteen percent. Rising disposable incomes, growing healthcare digitization, and government programs supporting personalized medicine in nations like China and India are all factors contributing to this industry's explosive growth. Both domestic and foreign businesses are taking advantage of these advantageous market conditions.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Outlook for Key Countries
United States Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Analysis and Trends
The USA’s market remains foundational owing to early market entry by major players and significant R&D investment. For example, in 2024 alone, U.S.-based genetic testing kit shipments experienced a 22% increase, directly contributing to the region’s leadership. Supportive regulations around genetic data privacy under HIPAA and increased public awareness further reinforce sustained growth. Companies like AncestryDNA and 23andMe continue to innovate, enhancing service scope and customer retention through AI-powered analytics and subscription services.
China Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Analysis and Trends
China’s market is expanding rapidly due to growing consumer health awareness and governmental focus on biotechnology innovation. The nationwide push towards digital healthcare integration and increasing partnerships between global and local firms have led to 28% year-over-year growth in device sales in 2024. Entities like Futura Genetics have been instrumental in introducing region-specific genetic panels, fostering adoption across urban and semi-urban populations.
Analyst Opinion
Adoption rates are accelerating due to enhanced affordability and consumer accessibility; for instance, unit shipments of genetic testing kits in the U.S. increased by 20% year-over-year in 2024, emphasizing demand-side expansion driven by direct purchasing models. Additionally, pricing models introduced in 2025 have reduced entry barriers by nearly 15%, sparking further market penetration.
Supply-side capacity expanded substantially in 2024 with leading facilities scaling production by over 25%, allowing market players to fulfill rising orders efficiently, contributing to sustained revenue growth amid surging demand.
Diverse use cases across health diagnostics, ancestry tracing, and lifestyle management continue to widen the market scope. In 2025, health-related applications accounted for over 55% of total revenue, driven by breakthroughs in identifying genetic predispositions to chronic diseases, which resonates with increasing consumer preventive healthcare focus.
Cross-border exports of genetic testing devices saw a surge of 18% in 2024, highlighting a global shift towards personalized medicine acceptance and reflecting heightened international demand, particularly in Europe and Asia Pacific.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Year: | 2025 | Market Size in 2025: | USD 3.85 billion |
| Historical Data for: | 2020 To 2024 | Forecast Period: | 2025 To 2032 |
| Forecast Period 2025 to 2032 CAGR: | 13.8% | 2032 Value Projection: | USD 9.75 billion |
| Geographies covered: |
|
||
| Segments covered: |
|
||
| Companies covered: | 23andMe, AncestryDNA, MyHeritage, Invitae Corporation, Gene by Gene, Futura Genetics, Helix OpCo, Nebula Genomics, CircleDNA, Orig3n | ||
| Growth Drivers: |
|
||
Uncover macros and micros vetted on 75+ parameters: Get instant access to report
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Growth factors
The growing consumer preference for tailored health insights more than 65% of buyers in 2024 stated that personalized healthcare advantages were their main incentive is one of the major growth drivers for the Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices market. Next-generation sequencing and AI-based data analysis tools are two examples of technological innovations that have significantly improved test accuracy and result turnaround times, which has increased market revenue.
Easy access to online distribution channels has been made possible by rising internet penetration and smartphone usage; in 2025, sales from online retailers will account for 61% of total market revenue. Finally, customer trust has increased as a result of key markets' increasing regulatory clarity regarding consumer privacy and data security, which has a favorable impact on industry growth dynamics.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Development
In January 2025, Datar Cancer Genetics (DCG) recently introduced the Target-MRD blood test, which is intended to detect and track molecular residual disease (MRD) in patients with solid organ malignancies. This test combines the use of personalized tumor-informed droplet digital PCR (dd-PCR) assay with tumor-agnostic next-generation sequencing (NGS).
In May 2025, A new direct-to-consumer genetic testing and personalized wellness solution has been launched through Hydreight Technologies Inc.'s VSDHOne platform. Hydreight Technologies Inc. is a rapidly expanding digital health platform that offers compliant mobile and telehealth services in all 50 U.S. states.
In July 2023, The pioneer of diagnostic information services, Quest Diagnostics, announced the release of its first user-initiated genetic test, which is presently only accessible at questhealth.com, the company's consumer health division. With cutting-edge technology and comprehensive support that includes individualized health assessments and access to genetic counseling, the new product, called Genetic Insights, helps people understand their possible risk of having specific inheritable health issues.
Key Players
23andMe
AncestryDNA
MyHeritage
Invitae Corporation
Gene by Gene
Futura Genetics
Helix OpCo
Nebula Genomics
CircleDNA
Orig3n
Market participants have turned to technical innovation and strategic mergers to strengthen their position in the market. By incorporating AI-driven genomics interpretation tools, for instance, 23andMe improved its competitive edge in 2025 and saw a 30% rise in user engagement. Similar to this, AncestryDNA increased the accuracy of ancestry tracing and membership renewals by 18% in the same year by using strategic partnerships to grow its global database.
Direct to Consumer Genetic Testing Devices Market Future Outlook
The Direct to Consumer (DTC) Genetic Testing Devices Market will have a bright future thanks to rising consumer awareness and the need for individualized medical care. Developments in artificial intelligence and genetic sequencing technology will improve the precision, comprehensiveness, and cost-effectiveness of genetic testing, opening up access to a wider range of people. Comprehensive whole-genome sequencing and the addition of microbiome and epigenetic analysis for more comprehensive health insights will become increasingly popular in the market.
However, the market’s growth will also depend on the resolution of ethical, regulatory, and data privacy challenges, with strict data protection laws and advanced encryption technologies becoming standard to maintain consumer trust. Emerging markets, especially in the Asia-Pacific region, will show significant growth due to rising income levels, education, and healthcare infrastructure improvements.
Overall, DTC genetic testing will become a cornerstone in personalized medicine and preventive healthcare, driving market expansion and innovation over the next decade. This evolution will be characterized by enhanced regulatory frameworks, technological breakthroughs, and growing consumer demand for actionable health insights.
Historical Analysis
An examination of the Direct to Consumer (DTC) Genetic Testing Devices Market's history shows a timeline characterized by important turning points and quick development. The origins of the market can be seen in the late 1990s, when the first genetic testing businesses started selling tests to customers directly via mail order and public relations. Key technological breakthroughs, such as the completion of the Human Genome Project in the early 2000s, catalysed growth by enabling greater understanding and accessibility of genetic information. The first wave of dedicated DTC genetic testing companies emerged in the mid-2000s, offering tests primarily focused on ancestry and genetic traits.
However, regulatory scrutiny increased around 2010 when the FDA began monitoring the clinical validity of tests, which initially slowed the market's growth. Concurrently, the cost of genetic sequencing declined dramatically, making tests more affordable and accessible to the general public. Over the last decade, advancements in genome sequencing, bioinformatics, and AI-driven analysis expanded the scope of tests to include health risk assessment, carrier status, and pharmacogenomics. Consumer interest surged both in ancestry and personalized health insights, further driving market demand.
By the early 2020s, online platforms dominated as the primary distribution channel. The market has grown substantially, particularly in North America, due to high consumer awareness, healthcare infrastructure, and active industry players. Global expansion has also begun, with rising interest and infrastructure development in emerging regions. Overall, the historical trajectory reflects a shift from niche ancestry testing to comprehensive health-focused genetic services, shaping the current robust and rapidly expanding DTC genetic testing market.
Sources
Primary Research interviews:
Healthcare practitioners (family physicians, oncologists, gynaecologists)
Molecular biologists and lab technicians
DTC genetic testing company executives (e.g., product managers, R&D heads)
Databases:
MEDLINE
Embase
Statista (non-firm, general database)
Magazines:
BioTechniques
Nature Biotechnology (magazine section)
MIT Technology Review (Biomedicine section)
Journals:
Genetics in Medicine
Journal of Personalized Medicine
Human Genetics
Newspapers:
The Guardian (Science/Health)
The Washington Post (Health/Science)
Financial Times (Healthcare/Technology)
Associations:
International Society of Genetic Genealogy (ISOGG)
European Society of Human Genetics (ESHG)
Personalized Medicine Coalition (PMC)
Share
Share
About Author
Manisha Vibhute is a consultant with over 5 years of experience in market research and consulting. With a strong understanding of market dynamics, Manisha assists clients in developing effective market access strategies. She helps medical device companies navigate pricing, reimbursement, and regulatory pathways to ensure successful product launches.
Missing comfort of reading report in your local language? Find your preferred language :
Transform your Strategy with Exclusive Trending Reports :
Frequently Asked Questions
Select a License Type
Joining thousands of companies around the world committed to making the Excellent Business Solutions.
View All Our Clients